Spinal Cord Injuries (SCI) are caused by trauma to the spinal cord that impairs physical function, mobility or feeling.
The majority of patients suffering from SCI have an intact spinal cord, but still have enough cellular damage to result in a loss of physical functioning.
The effects caused by SCI depend heavily on the type of injury and the level of injury. A spinal cord injury refers to any injury to the spinal cord that is caused by trauma. Spinal cord injuries often cause changes in strength, body function and movement.
The rationale of utilizing highly concentrated mesenchymal cells is to provide the patient with a treatment that stimulates his / her immune system, promotes cellular regeneration and improves symptoms associated with spinal cord injuries.
Cellular therapy utilizes regenerative stem cells targeted to specific areas in order to repair cellular damage that was caused from spinal cord injuries.
Also, this therapy helps control inflammation and promotes regeneration that may improve a SCI patient’s ability to move and feel.
The endovascular/intravenous treatment containing Adult Stem Cell should serve to complement the patient’s current treatment regimen or to promote healing when current treatment is not responding.
Published improvements include improved ASIA scores, improved bladder and/or bowel function, recovered sexual function, and increased muscle control.
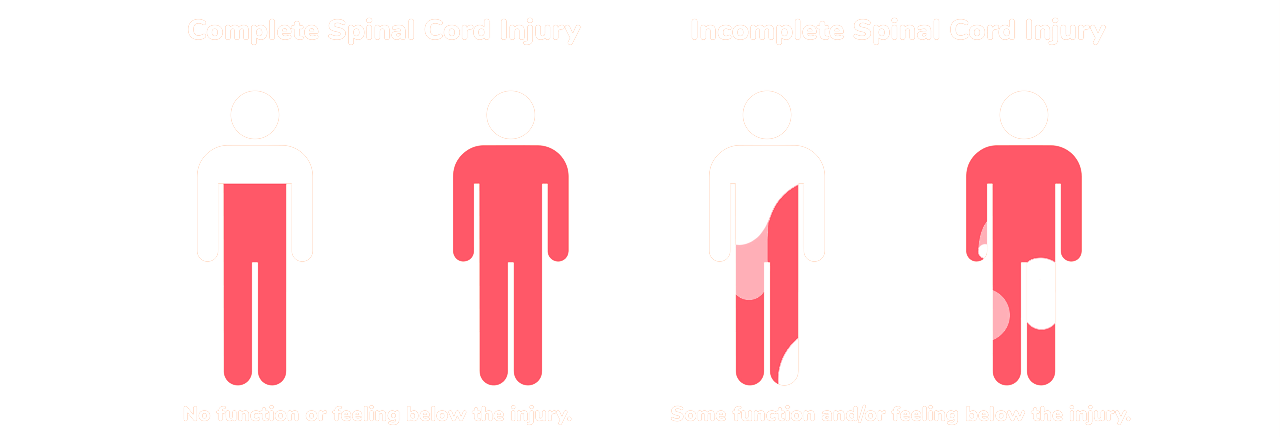
Spinal cord injuries can be described as various levels of incomplete, where complete means total loss of function.
Recent studies have focused on the use of adult stem cells for spinal cord injury patients. It has been discovered that introduction of mesenchymal stem cells either intralesionally or intravenously can be successful in improving functional recovery in chronic spinal cord injuries.
There are two types of SCI injuries: