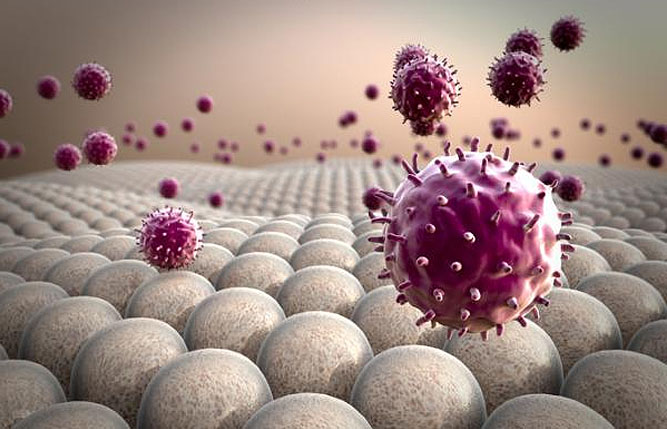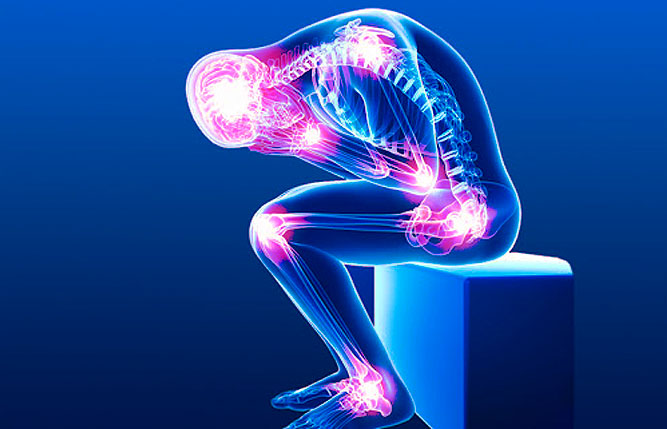
Autoimmune diseases are conditions in which the patient’s immune system generates cellular and antibody responses to substances and tissues normally present in the body. This might be restricted to one organ or involve a particular tissue in different places. As a result of this immune response, damage to different organs occurs.
Examples of autoimmune diseases that have responded to stem cell therapy either in animals or humans include rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and lupus. Stem cell therapy has been demonstrated to induce profound healing activity in animals with various forms of autoimmune disorders.
Autoimmune diseases are conditions in which the patient’s immune system generates cellular and antibody responses to substances and tissues normally present in the body. This might be restricted to one organ or involve a particular tissue in different places. As a result of this immune response, damage to different organs occurs.
Examples of autoimmune diseases that have responded to stem cell therapy either in animals or humans include rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and lupus. Stem cell therapy has been demonstrated to induce profound healing activity in animals with various forms of autoimmune disorders.
Stem cells and specifically, mesenchymal stem cells hone to inflamed tissue and start producing anti-inflammatory agents.
These mediators act locally and do not suppress the immune response of the patient’s whole body.
Additionally, mesenchymal stem cells induce the production of T regulatory cells, a type of immune cell whose function is to protect the body against immunological self-attack.